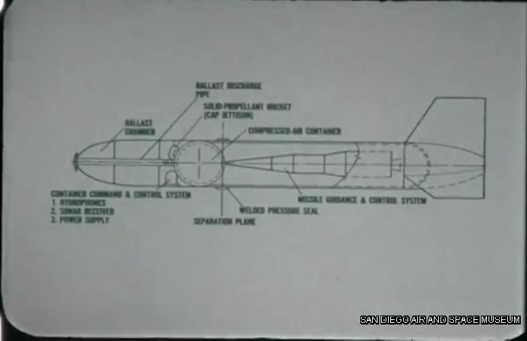
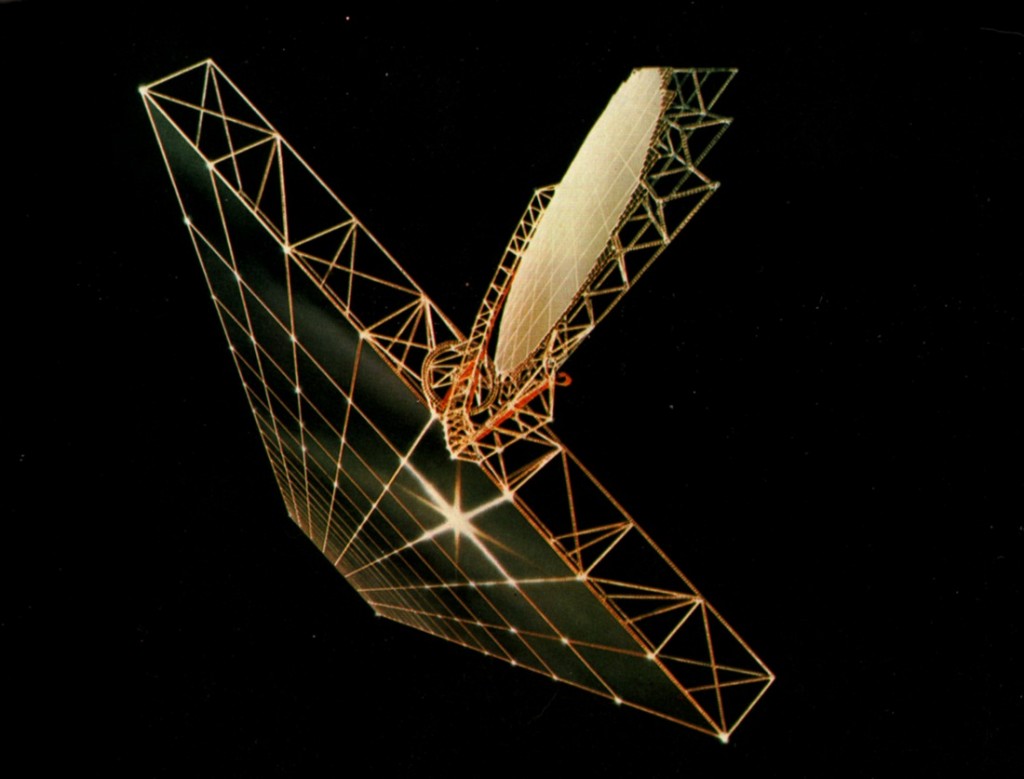
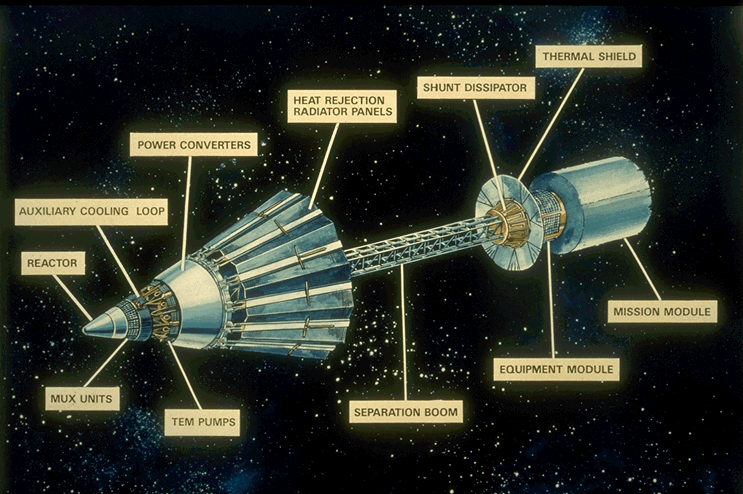
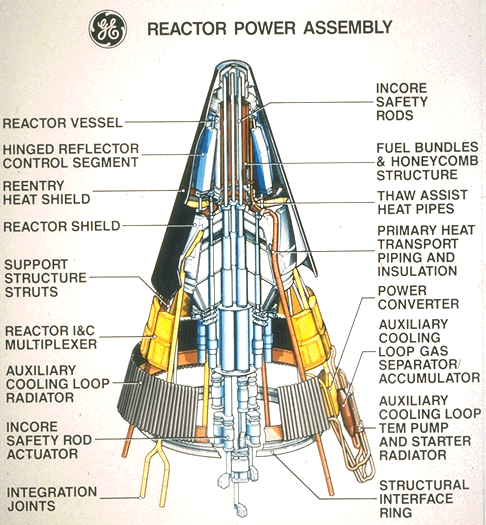
UPDATE: the deadline has come… these are now no longer for sale.
I am making available, for a limited time, four bound volumes of large format diagrams. These are 11X17 line-drawing CAD diagrams produced by yours truly, bound in red pressboard report covers (why? because that’s classy, that’s why).
I had not planned on releasing these, but I had also not taken into account the fact that the IRS will very soon be demanding a sizable income tax check from me. Ooops. So, my sudden financial panic is your opportunity to get a limited edition item. They will be available until some time on Thursday, March 20. At which point they will be gone forever. Each one will be hand inscribed with the number of the edition (“#1 of 5” or “#4 of 7,” whatever the case may be), with the numbering done via order in which orders are received. Also with my hand-enscribbled initials. (Because who knows, I might be famous someday.)
What I have:
1) BoMi: the complete set of diagrams created for the “Bomber Missile” articles for Aerospace Projects Review issues V2N3 and V2N4, a total of about 45 pages. Includes the MX 2276 from 1955, up through the SR-126 studies from 1957, Brass Bell, Convairs RoBo, Super Hustler, FISH; and Boeing Model 728 studies, among others. $45
2) BWB: The complete set of diagrams created for the V1N3 APR article on Blended Wing Body aircraft, 29 pages. Contains many jetliner concepts, along with such oddities as the Lockheed CL-1201,a giant nuclear powered VTOL assault transport concept. $40
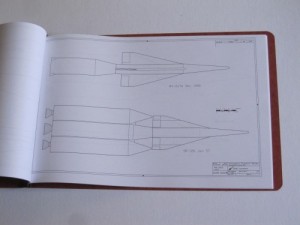
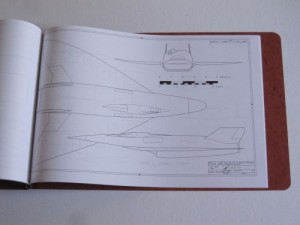
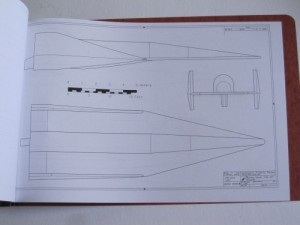
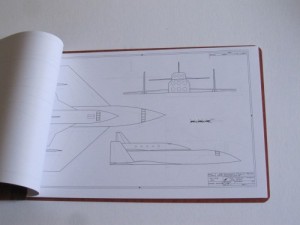
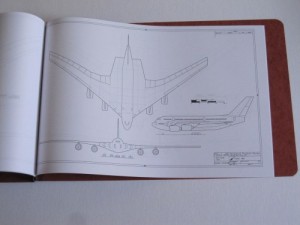
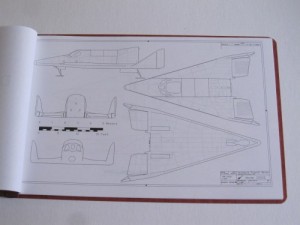
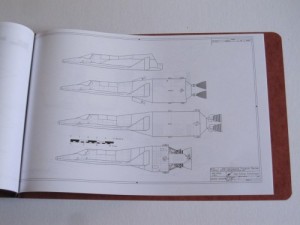
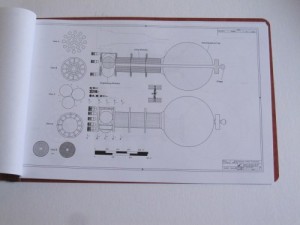
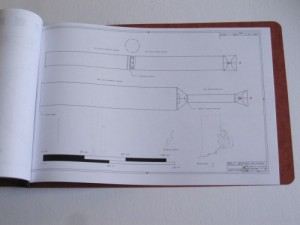
3) Model 2050E X-20 Dyna Soar: the diagrams from the not-yet released issue V3N4 APR article. These are the diagrams in their current state; some may change before I’m done with them. And some will not appear in the article. Includes not only the X-20, but also several proposed launch vehicles (including, I’m reasonably proud to say, the first publicly available accurate and detailed diagrams of the X-20 atop the Titan IIIc), layouts of test and operational versions of the DS with transstage, several small space stations designed expressly for DS servicing, and several high-energy transstage concepts. Also includes really quite good diagrams of the ASSET test vehicle and the X-37B spaceplane. 24 pages, $35
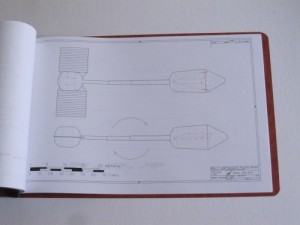
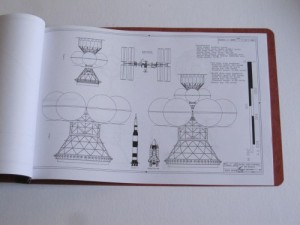
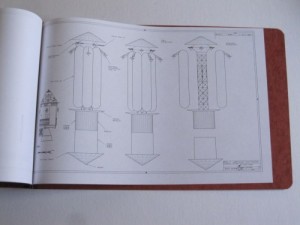
4) Nuclear Pulse Propulsion Starships: diagrams from my hopefully-forthcoming book on nuclear pulse propulsion. I really had not planned on releasing any of the diagrams prior to publication of the book, but what the heck: here are 14 pages showing several versions of the Enzmann Starship, the Dyson Starship, the BIS Daedalus, the Martin/Bond Worldships and the US Naval Academy “Longshot.” $30
Several of the X-20 and NPP diagrams have been formatted specifically for this release, and will not be otherwise released. And of course if I get mashed by a Mack truck or flattened by a meteorite, these diagram sets will be the only versions of these diagrams ever released. So, you know, there’s that…
————