In January I signed my very first book contract, for a heavily illustrated aerospace history text Yet To Be Publicly Described. The manuscript and all the diagrams were due to be turned in to the publisher in July. And then… Commie Cough comes along, book stores close, supply chains collapse. Perhaps surprisingly, the book was not cancelled, but instead delayed by one year. Sigh, oh well, okay.
So today, I signed a *second* book contract with the same publisher. This is for a slightly smaller text on a different subject, but similar in idea: a boatload of aerospace diagrams. Book One looks to have around 180 diagrams; Book Two will top out somewhere in the area of 120. This one has a due date of January, 2021.
If you like the US Aerospace Projects publications I’ve put out, then you’ll go bonkers for these books.
An aside: for public discussion purposes, the first book is “Book X.” The second book would thus be either “Book Y” or perhaps “Book XX.” In which latter case if and when I sign a third book contract, that would should prove quite interesting.
Protected: GE Interplanetary Spacecraft Concept crowdfund
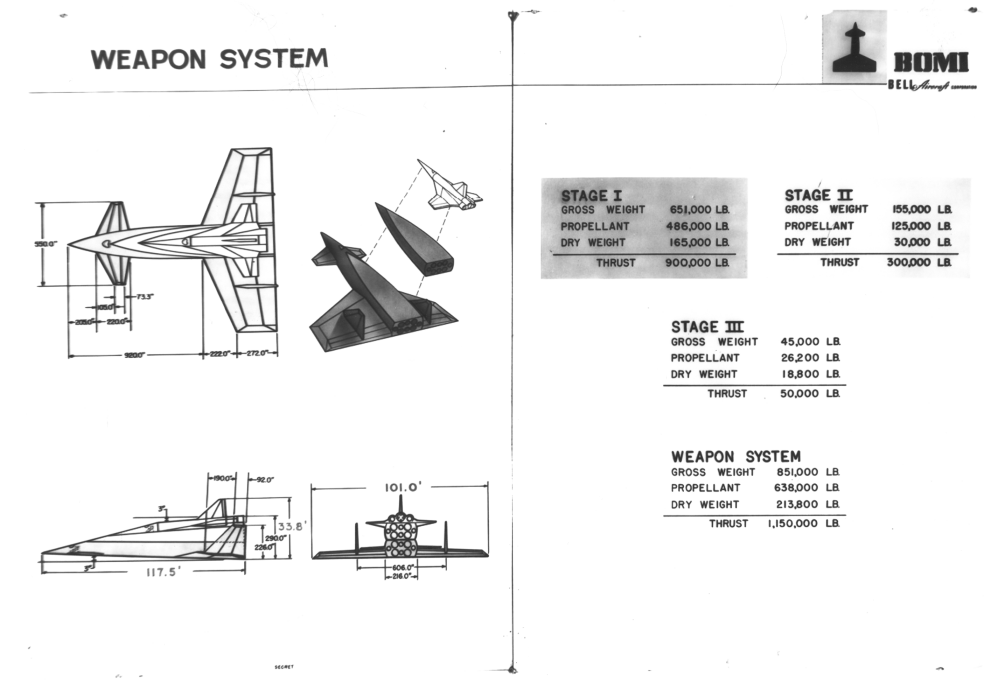
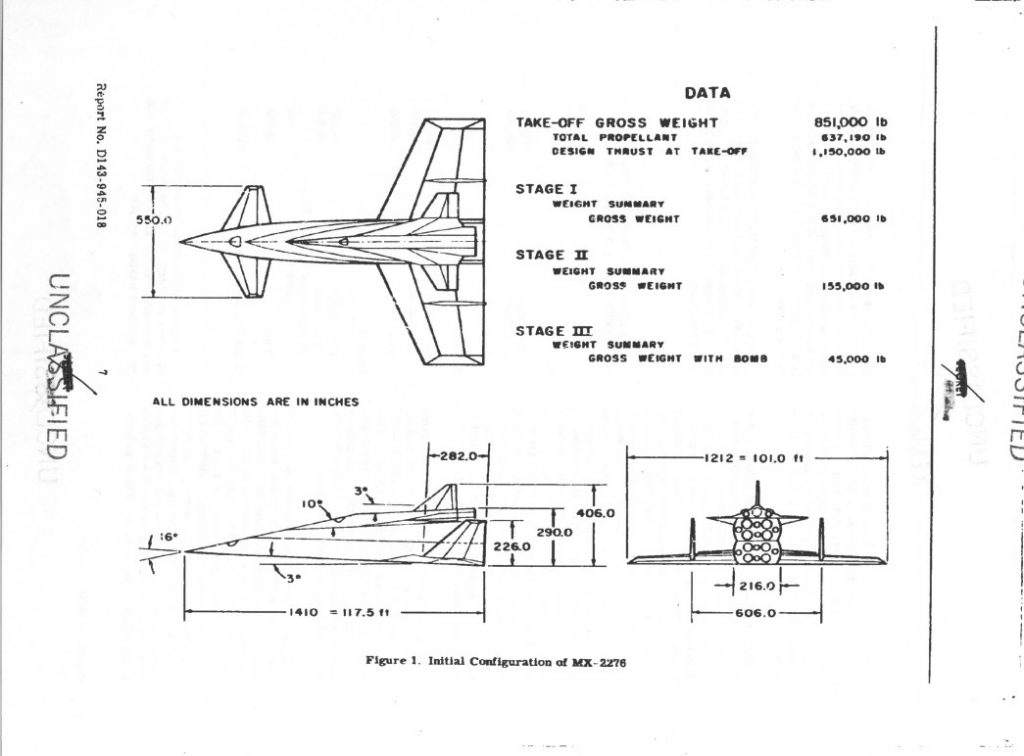
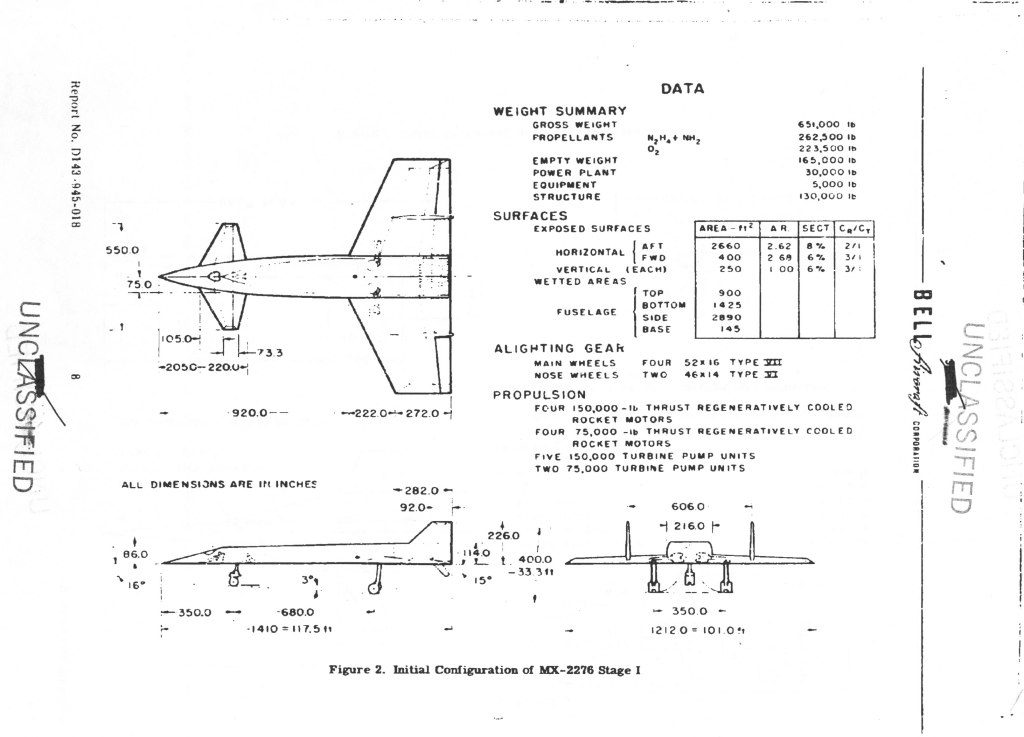
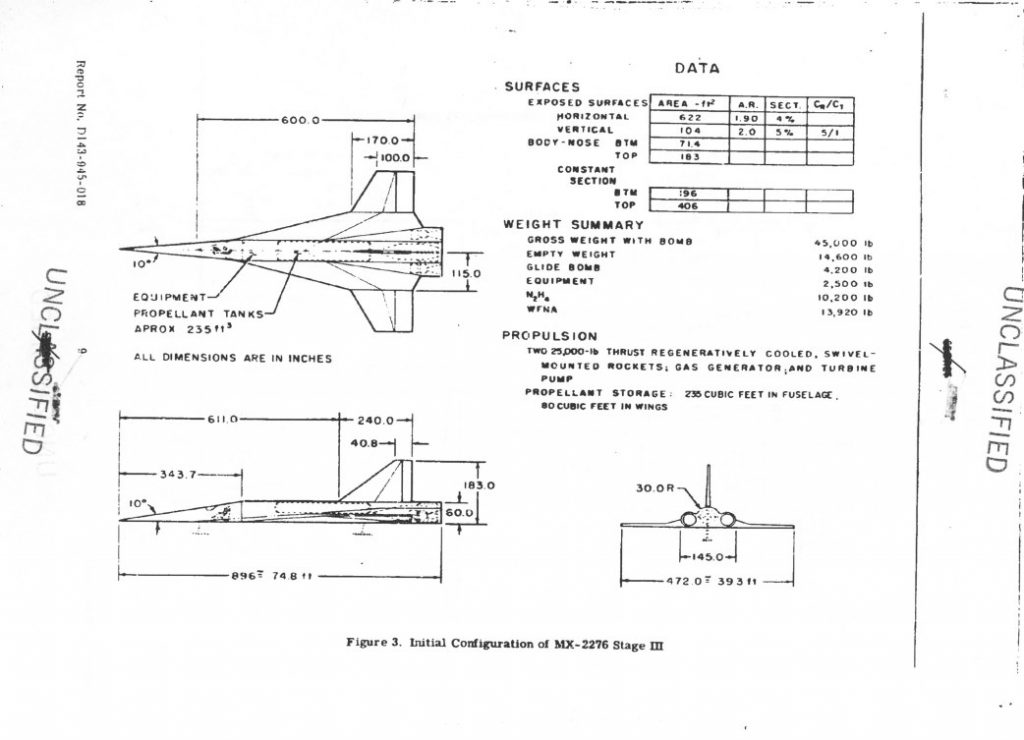
Before the Convair Atlas ICBM proved that it was possible for a rocket to reach out across the world and deposit some canned sunlight reliably close to commie targets, it was understood that the only way to accomplish the task was with pilots and bombardiers. But by the mid 1950’s the idea of subsonic manned bombers sneaking into the heart of the Soviet Union without getting swatted was starting to seem nonsensical. So Bell Aircraft, under the direction of former V-2 program director Walter Dornberger, dreamed up the MX-2276: a three-stage manned rocket bomber. Looking akin to an evolved Sanger Antipodal Bomber, the MX-2276 used two manned and winged stages, with an unmanned expendable stage in between. The final stage would carry a single gliding nuclear warhead deep into the USSR, using the human crew to attain some measure of accuracy.
But then the Atlas came along and ruined all that.
The idea persisted, however, turning first into the Bomber Missile (BoMi) then the Rocket Bomber (RoBo) then Dyna Soar. With each step it became less fantastical, and also less of a dedicated weapon system; by the end of the Dyna Soar, it was a one-man experimental re-entry vehicle launched by a fully expendable Titan IIIC. Since then the idea of a “rocket bomber” has popped up from time to time, but never with the level of seriousness displayed in the mid/late 1950’s. For more on the whole BoMi program, see Aerospace projects Review issues V2N2, V2N3 and V2N4. APR issue V3N4 gives a pretty complete rundown of the final Model 2050E Dyna Soar.
A piece of Boeing artwork depicting several early jetliner concepts. The B-47 design heritage is obvious. This piece was on ebay a while back, and while it wasn’t one that I won, I snagged a decently-high rez scan from the listing and have made it available to all $4 and up APR Patrons and Monthly Historical Document Subscribers. it has been uplosded into the June 2020 folder at Dropbox for those subscribers.
If this sort of thing is of interest, sign up either for the APR Patreon or the APR Monthly Historical Documents Program.
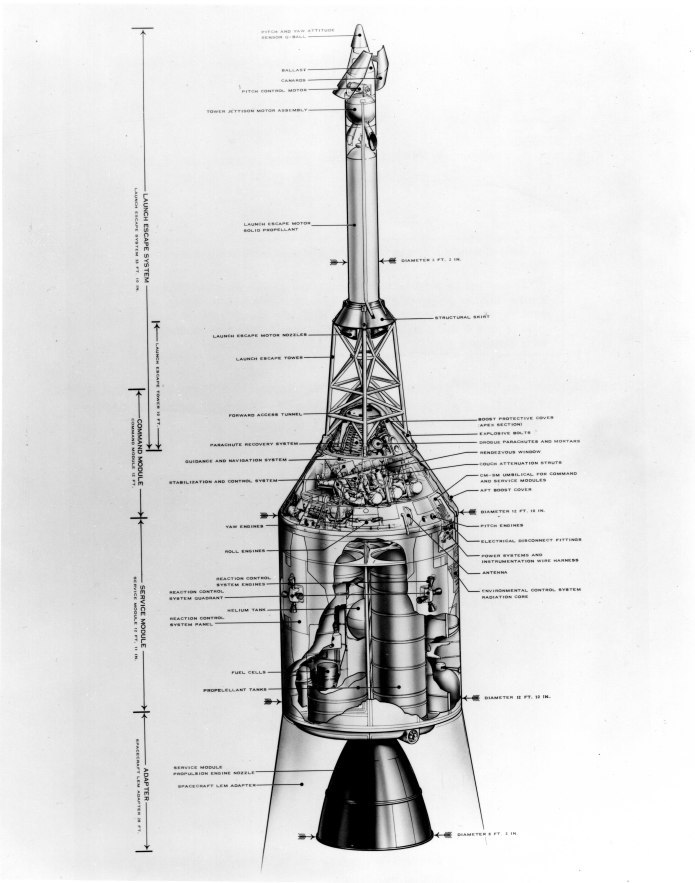
Just in from ebay, a vintage black & white cutaway illustration of the Apollo CSM. The original has been scanned at 600 dpi (it’s clear enough for that high of a resolution) and made available to subscribers of the APR Patreon and the Monthly Historical Documents Program at above $10/month as an “extra.”
If this sort of thing is of interest, sign up either for the APR Patreon or the APR Monthly Historical Documents Program.
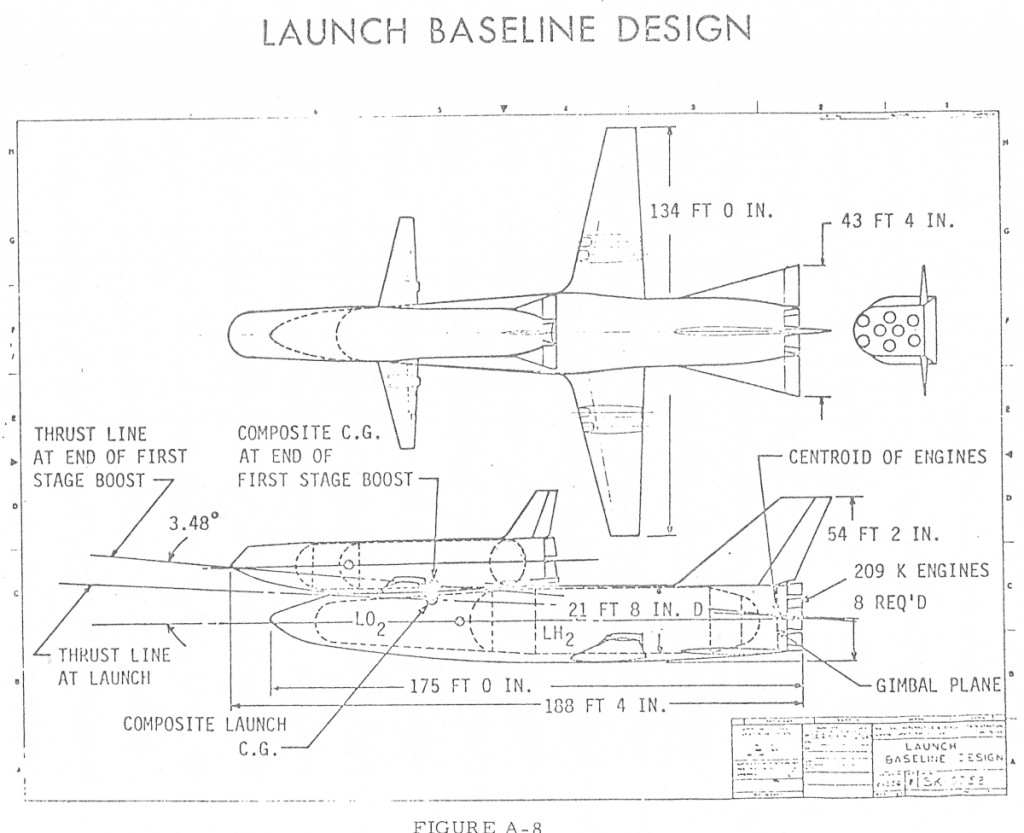
In 1969, Maxime Faget of NASA-Manned Spacecraft Center (later renamed Johnson Space Center) produced a concept for a simplified version of the Space Shuttles then being designed. The idea at the time was that the Shuttle would be a two-stage vehicle, both being fully reusable manned flyback vehicles. The Orbiter would be much larger than the Orbiter that actually got built because it included substantial hydrogen/oxygen tankage. The boosters were generally *vast* vehicles larger than the C-5 Galaxy meant to fly higher and faster than the X-15. Optimistic to be sure. Faget’s “DC-3” design had the same basic architecture but attempted to produce a smaller, cheaper, less complex and more realistic design. The design, produced in-house at NASA, was picked up by both North American and McDonnell Douglas, who designed their own variations on the theme.
Here is the basic configuration of the NASA-MSC “DC-3:”
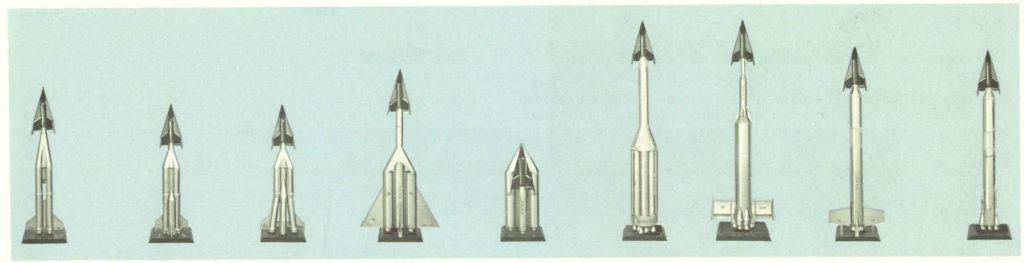
A photo montage of Boeing display models showing a range of launch vehicles intended to put the early (1959) Dyna Soar into orbit. The three at left are clusters of Minuteman ICBM boosters; the next two are larger solid rocket motor clusters. The next is a Saturn I booster, followed by an all-new recoverable liquid rocket booster, the Titan II and the Atlas/Centaur. The Titan II design was chosen, though it could not actually get the Dyna Soar into a true orbit. To do that, solid rocket boosters needed to be strapped to the sides of the Titan II… leading to the creation of the Titan III.
Another Chinook derivative, the Model 167 was substantially further from the original. It was larger and had an additional turboshaft engines… and moved all three of them forward, *presumably* for balance reasons. This was from the era when it seemed like a good idea to operate commercial helicopter “buses” from rooftop heliports in major cities, generally to shuttle passengers either from one city to another nearby one, or from the heart of an urban area to an outlying airport. It’s a little difficult to be sure, but it looks like the Model 167 had retractable landing gear.
A 1966 Boeing concept for a civilian version of the Chinook. Viet Nam veterans I’ve known who rode in Chinooks of that era have stories that make me suspect that *substantial* structural stiffening would have been required for such a craft to be fully accepted by the public; apparently, looking forward towards the cockpit and watching the while cabin twist back and forth was slightly disconcerting. A cruise speed of 200 mph seems slightly optimistic.