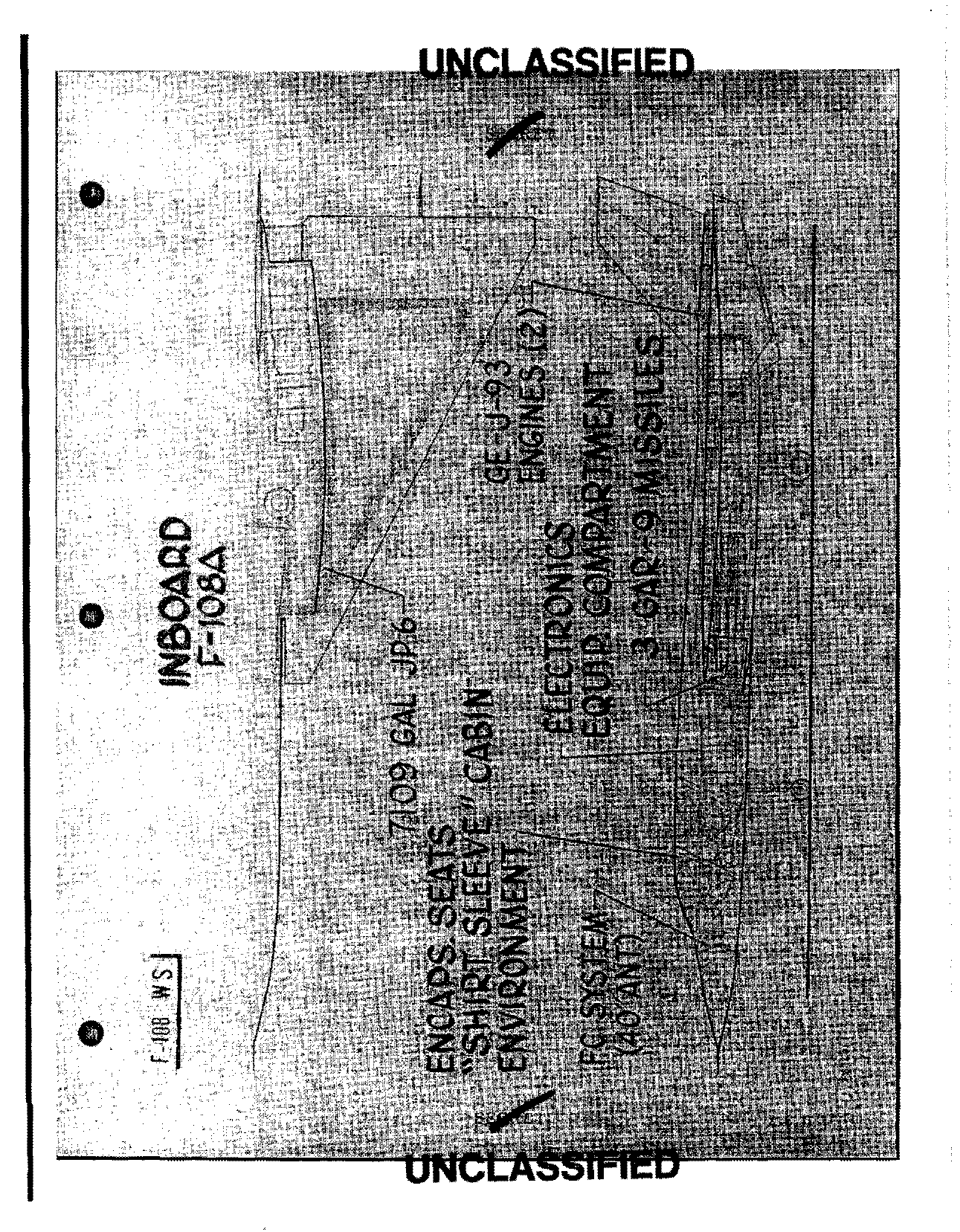
Sigh. It’s sad to think that in many ways the 1970’s were more forward thinking than today. Solar Power Satellites the size of Manhattan, space colonies the size of small states. Today… apart from SpaceX, about the most you can hope for is ever more social media. Until, of course, you get deplatformed.
Below is a piece of NASA-Ames art depicting the interior of an Island 3 colony. The full size version is downloadable HERE. This was intended to be a cylinder 5 miles or so in diameter by 20 long, rotating along the long axis to generate “gravity.” In this design, fully one third of the “land area” was given over to windows that would bring in sunlight via mirrors. Other notions included mounting strips of very powerful artificial light on the “ground” facing up to light the other side (this was the Babylon 5 approach), mounting strips of artificial light along the central axis pointing outwards, having external parabolic mirror beam sunlight through the central axis and reflected or diffused outwards. In order for an island 3 habitat like this to be dynamically stable, you’d need two of them, side by side, rigidly linked at the hubs. This would counter the torque and prevent the cylinders from converting rotation around the long axis into end-over-end tumbling, which is the natural response of something like this (experiment: try to spin a pencils around the long axis. You will inevitably end up with it tumbling)

The NASA art below shows an exterior view of a complete colony.The habitats would need to be pretty close to the same mass, but otherwise their interiors could be very different… one could replicate, say, farmland and meadows and such with small towns scattered about; the other could have forests and large cities. One could be in winter, the other in summer. The full-rez is downloadable HERE.

There is a ring of “cans” around the end of each habitat. These are the agricultural units for the habitat; each independently spin around their own axis, generating the level of artificial G appropriate to grow wheat or corn or weed or hay or whatever is needed. Being smaller in radius, Coriolis effects would be substantially more noticeable; but as plants don’t care, and the job of agriculture will probably be done by robots, it doesn’t matter much. Each farm would be pretty well closed off from the others, so if some sort of blight were to pop up, chances are good it could be contained.
A few years ago I had a notion for a book – half technical descriptions, half manifesto/screed – about megaprojects. A description of not only what mankind could do given time and energy, but what mankind *should* do in time. As with a lot of things, this books got squashed by the realization that its already been done (gosh, thanks Isaac Arthur), but I still kinda want to 3D CAD model one of these things. I’ve not thought about that book in some years… got a hundred pages into it, I think. Shrug.