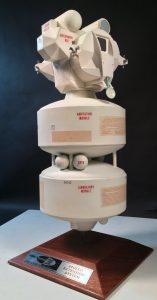
This art was posted a decade ago. But behold! Now there’s dimensional and weight data. Woo.
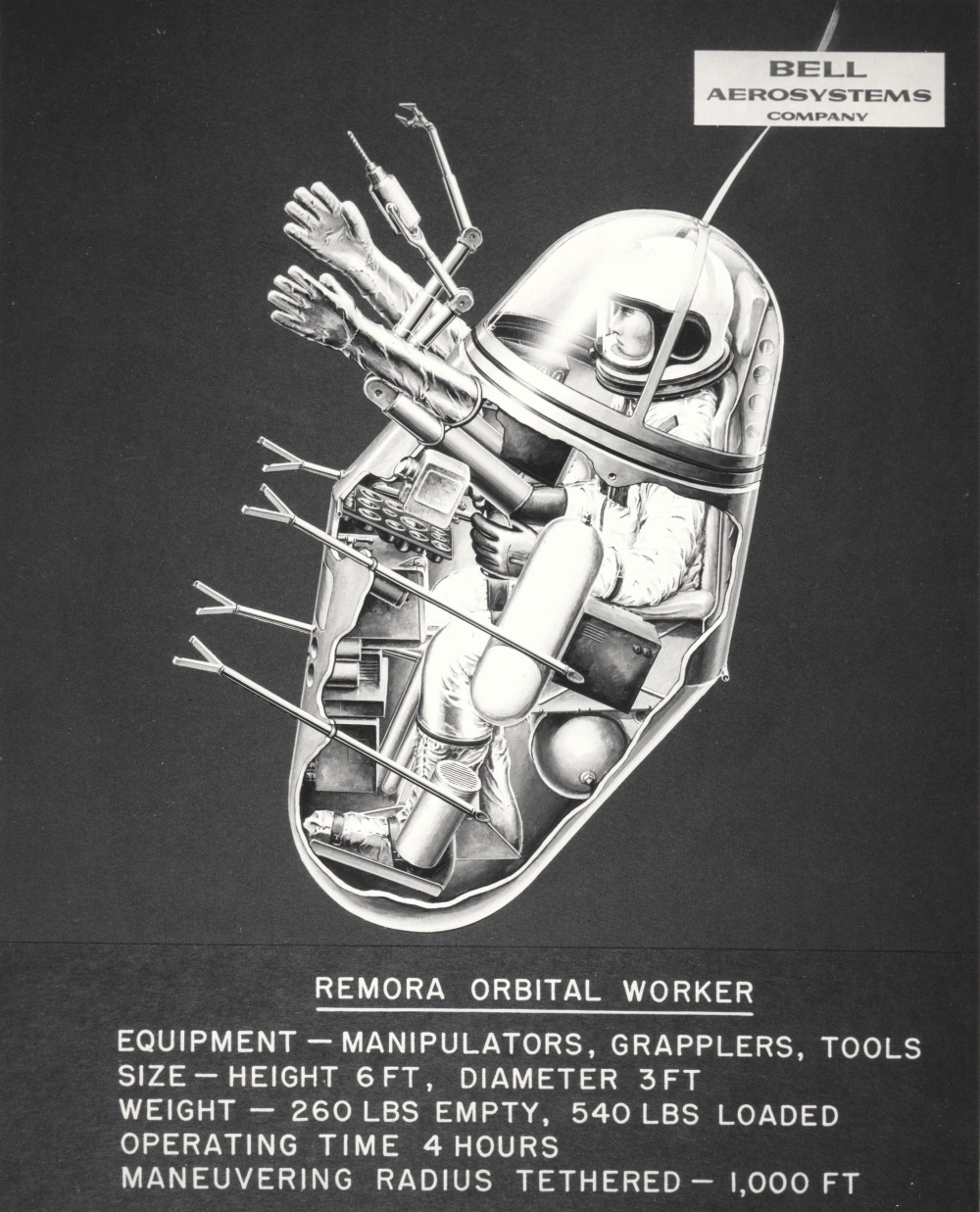
An early-1960’s idea for a one-man “space pod.” Similar in concept to von Braun’s “Bottle Suit,” the Remora would allow an astronaut to work in a more comfortable setting than a full pressure suit, while giving the astronaut more tools and greater protection from radiation, meteoroids and other space hazards.
The name “Remora” comes in part from the fact that the “suits” would not, unlike normal EVA suits, have to be put all the way through an air lock. Instead, the “head” of the Remora would enter a small port on the spacecraft, lock in, the pressure would equalize and the transparent dome would open allowing the astronaut to climb right out. The pressure in the spacecraft/space station would be the same as that within the Remora, meaning no prebreathing and no dangerous and time consuming steps up and down in pressure. The art shows the astronaut wearing a pressure suit; this would presumably be a safety measure in case the Remora was breached. So long as the Remora stayed pressurized, the astronauts suit could have had little to no relative pressure, meaning that it would not be stiff and difficult to work in. The Remora was to be equipped with a reaction control system of some kind, but exactly what remains unclear. Options would include:
1: Cold gas, like pressurized nitrogen
2: Monopropellant like hydrogen peroxide or hydrazine
3: Bipropellant, either hypergolic storables or something like hydrogen peroxide/kerosene. Cryogens seem unlikely.
The Remora was clearly meant to remain tethered to its spacecraft/space station. One wonders if the astronaut was supposed to remove his suit gloves before putting his hands into the external gloves of if the one would fit in the other. Additionally, it seems like there should have been little pressure doors on the inside of the glove in case a finger gets punctured.
A vastly higher resolution version of this art is HERE.